The term `Palestine' was originally a designation of an area of land in southern Canaan which the people known as the Philistines occupied a very small part of. The Canaanites, Canaanite-Phoenicians, and the Israelites, among others, established themselves in the area much earlier.Khalil Beidas
In modern times, the first person to self-describe Palestine's Arabs as "Palestinians" was Khalil Beidas in 1898, followed by Salim Quba'in and Najib Nassar in 1902.While the State of Israel was established on 15 May 1948 and admitted to the United Nations, a Palestinian State was not established. The remaining territories of pre-1948 Palestine, the West Bank – including East Jerusalem- and Gaza Strip, were administered from 1948 till 1967 by Jordan and Egypt, respectively.
Who lived in Israel first : The oldest fossils of anatomically modern humans found outside Africa are the Skhul and Qafzeh hominids, who lived in northern Israel 120,000 years ago. Around 10th millennium BCE, the Natufian culture existed in the area.
How old is Palestine
Early humans arrived in the Fertile Crescent and Palestine about 500,000 years ago. Settled life there began between 12,500 and 9,500 BCE, when the semi-sedentary Natufian culture (named after Wadi Natuf, west of Ramallah) developed.
Are Palestine’s Muslims : Close to 99 per cent of Palestinians are Muslims, with Christians making up less than 1 per cent of the population (PCBS, 2017) with small numbers of members of other communities including around 400 Samaritans resident in the West Bank.
More recent studies since 2017 have found that Palestinians are primarily descended from ancient Levantines present in what is today Israel and Palestine, dating back at least 3700 years.
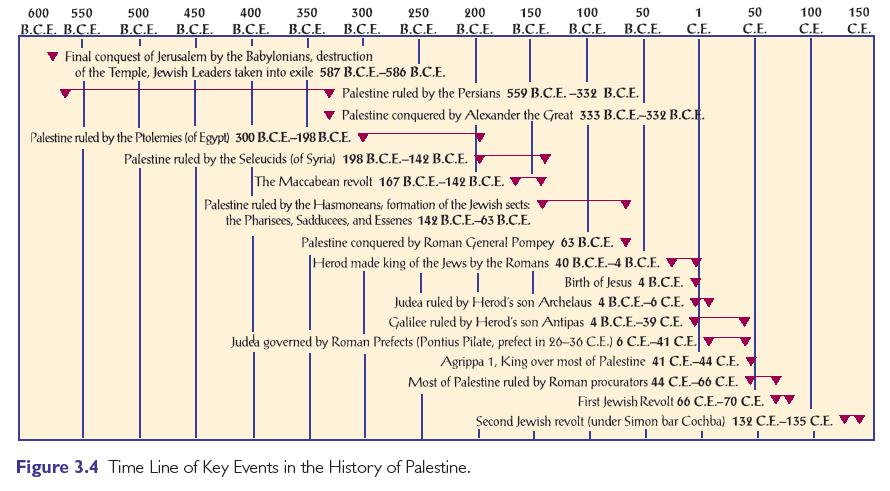
At the time of Jesus, Palestine (the Holy Land) was still part of the Roman Empire, and Roman law and customs were being imposed on the Jewish people. The Jews didn't like the Romans and there was always a great deal of tension between them. The Roman Emperor was called Caesar.
Who brought Islam to Palestine
ʿUmar ibn al-Khattāb
Islam was first brought to the region of Palestine during the Early Muslim conquests of the 7th century, when the Rashidun Caliphate under the leadership of ʿUmar ibn al-Khattāb conquered the Shaam region from the Byzantine Empire. The Muslim army conquered Jerusalem, held by the Byzantine Romans, in November, 636.Archaeologic and genetic data support that both Jews and Palestinians came from the ancient Canaanites, who extensively mixed with Egyptians, Mesopotamian, and Anatolian peoples in ancient times. Thus, Palestinian-Jewish rivalry is based in cultural and religious, but not in genetic, differences.Zachary Foster in his doctoral dissertation wrote that "Most scholars believe the Roman Emperor Hadrian changed the provincial administrative name of Judaea to Palestine to erase the Jewish presence in the land," opining that "it's equally likely the name change had little to do with Jew hatred and more to do with …
What we now call Palestinians are for the most part descendants of groups who have been in the Near East for four thousand years, at least. A branch of the Canaanites became Jews, while others became Nabataeans and Phoenicians.
What is Palestinian DNA : Admixture analysis in the same study inferred that Palestinian DNA resembled the mix of Jordanians, Syrians, Lebanese, and Druze very closely, whereas Saudis showed far more Arabian and Subsaharan African DNA and far less Eastern Mediterranean DNA.
Where are Palestinian people originally from : ancient Canaanites
Archaeologic and genetic data support that both Jews and Palestinians came from the ancient Canaanites, who extensively mixed with Egyptians, Mesopotamian, and Anatolian peoples in ancient times.