Conidium is a fungal spore that is associated with asexual reproduction. Conidium develops on either the side of the hyphae or on top of it. Sometimes, these spores produce on the structures known as conidiophores. Conidiophores produce conidium spores.yeasts
Unicellular fungi (yeasts) cells form pseudohyphae from individual yeast cells. In contrast to molds, yeasts are unicellular fungi. The budding yeasts reproduce asexually by budding off a smaller daughter cell; the resulting cells may sometimes stick together as a short chain or pseudohypha (Figure 5.3.Following a period of intensive growth, fungi enter a reproductive phase by forming and releasing vast quantities of spores. Spores are usually single cellsproduced by fragmentation of the mycelium or within specialized structures (sporangia, gametangia, sporophores, etc.).
What are fungi closest related to : Animals and fungi are each other's closest relatives: congruent evidence from multiple proteins.
Where does asexual reproduction occur in fungi
Almost all fungi reproduce asexually by producing haploid spores through mitosis and releasing those spores via the fruiting body of the fungi.
What is the asexual structure of fungi known as : Conidia and sporangiospores are the two primary asexual spore types produced by fungi. They can be separated from one another by the mechanisms that lead to their formation and by the morphology of the sporophore that creates them. Asexual spores include arthrospores, conidia, chlamydospores, and sporangiospores.
Fungi reproduce asexually by fragmentation, budding, or producing spores. Fragmentation: Mycelial fragments can form new colonies. Mycelial fragmentation occurs when the mushroom mycelium separates into fragments and each component grows into a separate mycelium. Somatic cells in yeast form buds.
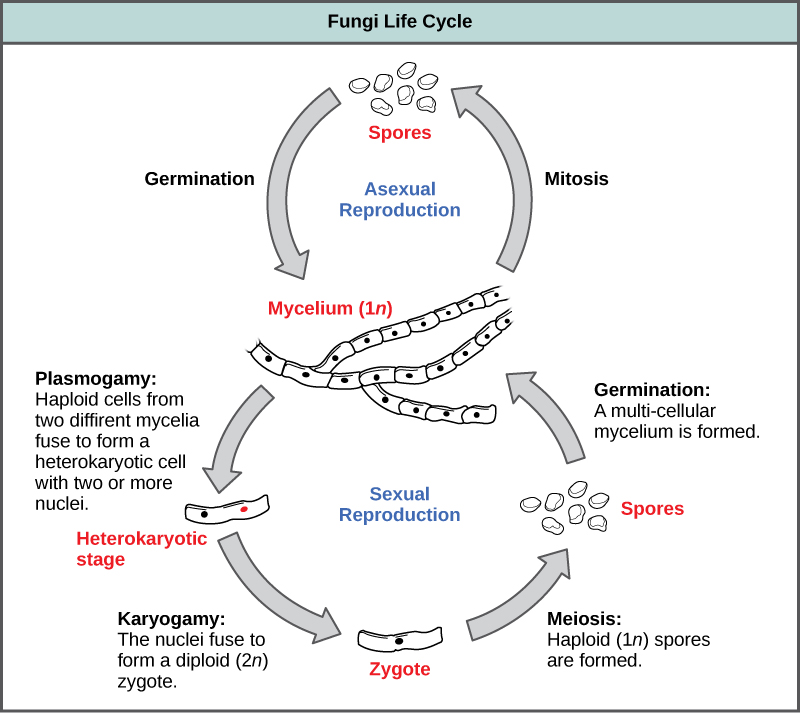
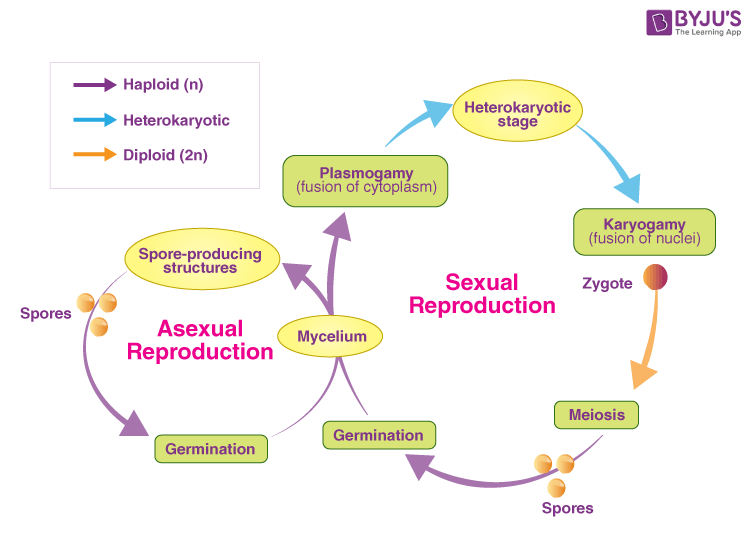
Fungi usually reproduce both sexually and asexually. The asexual cycle produces mitospores, and the sexual cycle produces meiospores. Even though both types of spores are produced by the same mycelium, they are very different in form and easily distinguished (see above Sporophores and spores).
What are the structures for fungi reproduction
Following a period of intensive growth, fungi enter a reproductive phase by forming and releasing vast quantities of spores. Spores are usually single cells produced by fragmentation of the mycelium or within specialized structures (sporangia, gametangia, sporophores, etc.).Most fungi reproduce by forming spores that can survive extreme conditions such as cold and lack of water. Both sexual meiotic and asexual mitotic spores may be produced, depending on the species and conditions.Most fungi reproduce by forming spores that can survive extreme conditions such as cold and lack of water. Both sexual meiotic and asexual mitotic spores may be produced, depending on the species and conditions.
spores
Almost all fungi reproduce asexually by producing spores. A funga l spore is a haploid cell produced by mitosis from a haploid parent cell. It is genetically identical to th e parent cell . Fungal spores can develop into new haploid individuals without being fertilized.
What are the asexual structures of fungi : Fungi reproduce asexually by fragmentation, budding, or producing spores. Fragments of hyphae can grow new colonies. Mycelial fragmentation occurs when a fungal mycelium separates into pieces with each component growing into a separate mycelium. Somatic cells in yeast form buds.
Does fungi have asexual reproduction : Fungi usually reproduce both sexually and asexually. The asexual cycle produces mitospores, and the sexual cycle produces meiospores. Even though both types of spores are produced by the same mycelium, they are very different in form and easily distinguished (see above Sporophores and spores).
What is an asexual reproductive structure formed in fungi and bacteria
Spores are haploid unicellular bodies that are produced as a result of sexual or asexual reproduction in eukaryotic organsims such as algae, bacteria, fungi and some plants. The process of formation of spores is referred to as sporogenesis.
Asexual spores of higher fungi are called conidia, and although there is great variety in conidial form and function, all conidia represent nonmotile asexual propagules that are usually made from the side or tip of specialized sporogenous cells and do not form through progressive cleavage of the cytoplasm.Fungi usually reproduce both sexually and asexually. The asexual cycle produces mitospores, and the sexual cycle produces meiospores. Even though both types of spores are produced by the same mycelium, they are very different in form and easily distinguished (see above Sporophores and spores).
What structure do fungi use to reproduce : Most fungi reproduce by forming spores that can survive extreme conditions such as cold and lack of water. Both sexual meiotic and asexual mitotic spores may be produced, depending on the species and conditions.