The first written records referring to Palestine emerged in the 12th-century BCE Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt, which used the term Peleset for a neighboring people or land. In the 8th century BCE, the Assyrians referred to a region as Palashtu or Pilistu.The term Palestine first appeared in the 5th century BCE when the ancient Greek historian Herodotus wrote of a "district of Syria, called Palaistinê" between Phoenicia and Egypt in The Histories.Palestine
Under the British Mandate (1920–1948), the whole region was known as Palestine.
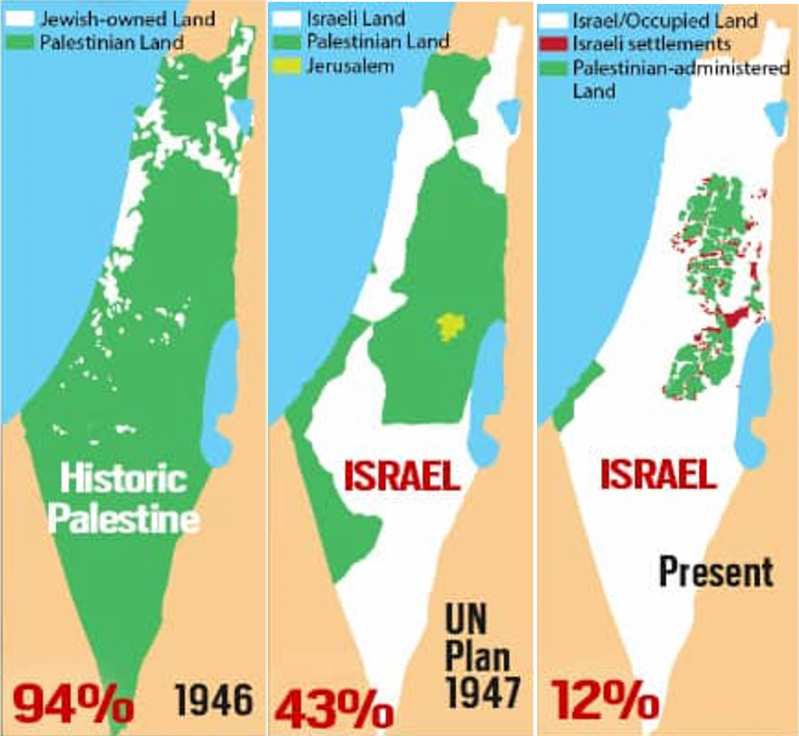
How old is Palestine as a country : In 1988 the Palestine National Council meeting in Algiers proclaimed the establishment of the State of Palestine.
What was Palestine called in 1946
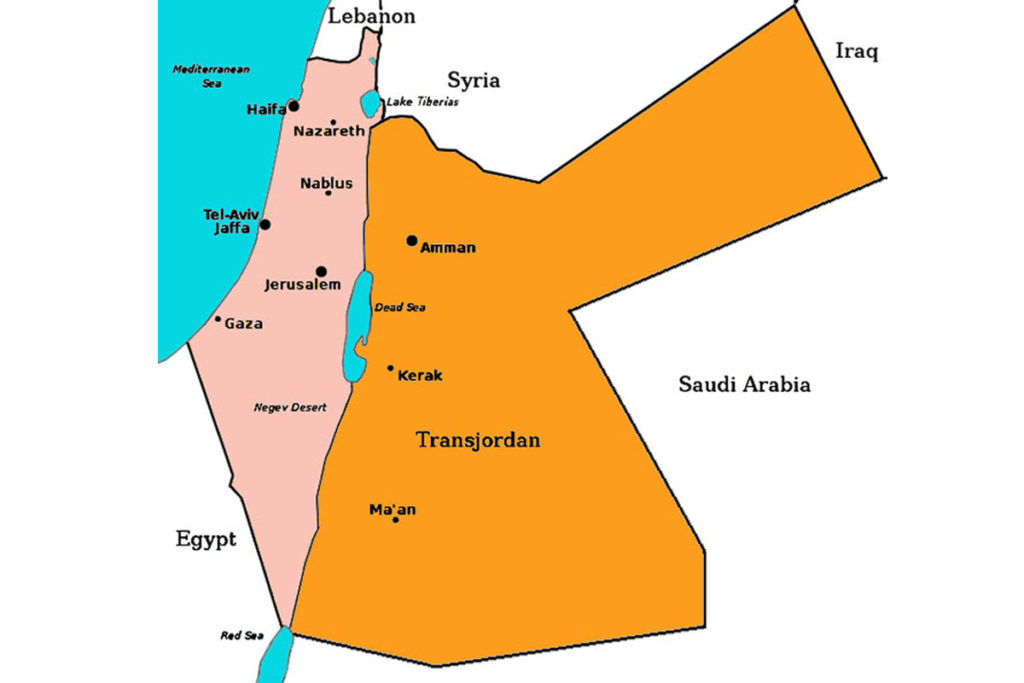
The short answer is that it remained under the British Mandate for Palestine until 1946, when it became the independent kingdom of Transjordan, later renamed Jordan. Western Palestine remained under the Mandate until May 1948.
Are Palestine’s Muslims : Close to 99 per cent of Palestinians are Muslims, with Christians making up less than 1 per cent of the population (PCBS, 2017) with small numbers of members of other communities including around 400 Samaritans resident in the West Bank.
Judea
This country received the name of Palestine, from the Philistines, who dwelt on the sea coast: it was called Judea, from Judah: and is termed the Holy Land, being the country where Jesus Christ was born, preached his holy doctrines, confirmed them by miracles, and laid down his life for mankind.
Syria Palaestina
Syria Palaestina (Koinē Greek: Συρία ἡ Παλαιστίνη, romanized: Syría hē Palaistínē [syˈri.a (h)e̝ pa.lɛsˈt̪i.ne̝]), or Roman Palestine, was a Roman province in the Palestine region between the early 2nd and late 4th centuries AD.
What was Palestine called in the Bible
The name was familiar to their ancient neighbours, occurring in Egyptian as Purusati, in Assyrian as Palastu, and in the Hebrew Bible as Peleshet (Exodus 14:14; Isaiah 14:29, 31; Joel 3:4). In the English authorized version, Peleshet is rendered Palestina or, in Joel only, Palestine.In 1917, in order to win Jewish support for Britain's First World War effort, the British Balfour Declaration promised the establishment of a Jewish national home in Ottoman-controlled Palestine.The Land of Israel (Hebrew: אֶרֶץ יִשְׂרָאֵל, Modern: ʾEreṣ Yīsraʾel, Tiberian: ʾEreṣ Yīsrāʾēl) is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine.
In November 1988, the PLO legislature, while in exile, declared the establishment of the "State of Palestine".
Is Palestine mentioned in the Quran : The Quran does not mention Palestine even once.
Are Palestine’s Sunni or Shia : Sunni Muslims
The U.S. government estimates the total Palestinian population at 3 million in the West Bank and 2 million in the Gaza Strip (midyear 2022). According to the U.S. government and other sources, Palestinian residents of these territories are predominantly Sunni Muslims, with small Shia and Ahmadi Muslim communities.
Is Palestine Greek or Roman
The word Palestine derives from Philistia, the name given by Greek writers to the land of the Philistines, who in the 12th century bce occupied a small pocket of land on the southern coast, between modern Tel Aviv–Yafo and Gaza.
At the time of Jesus, Palestine (the Holy Land) was still part of the Roman Empire, and Roman law and customs were being imposed on the Jewish people. The Jews didn't like the Romans and there was always a great deal of tension between them. The Roman Emperor was called Caesar.The word Palestine derives from Philistia, the name given by Greek writers to the land of the Philistines, who in the 12th century bce occupied a small pocket of land on the southern coast, between modern Tel Aviv–Yafo and Gaza.
Why was Palestine given to Israel in 1948 : Background. The 1948 War came as the culmination of 30 years of friction between Jews and Arabs during the period of British rule of Palestine when, under the terms of the League of Nations mandate held by the British, conditions intended to lead to the creation of a Jewish National Home in the area were created.