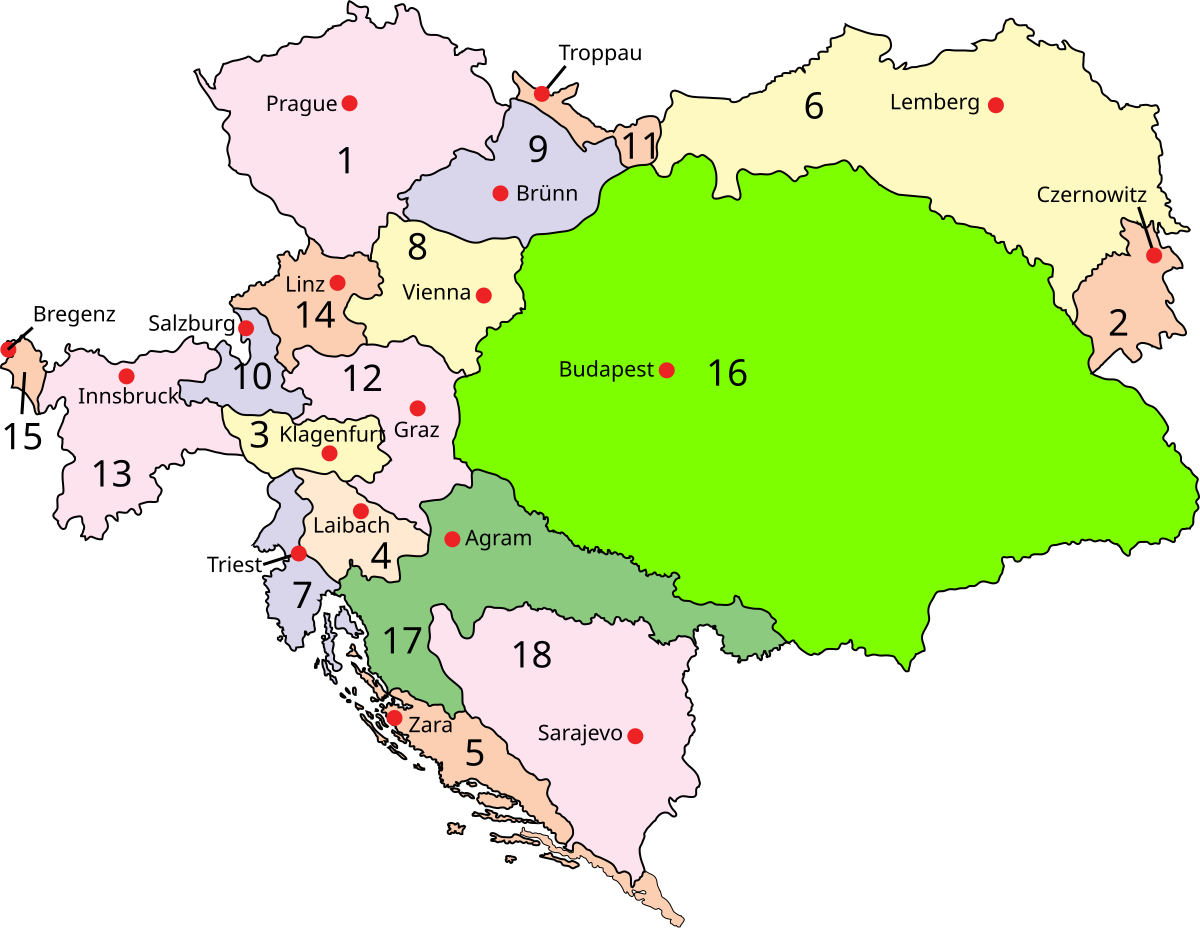
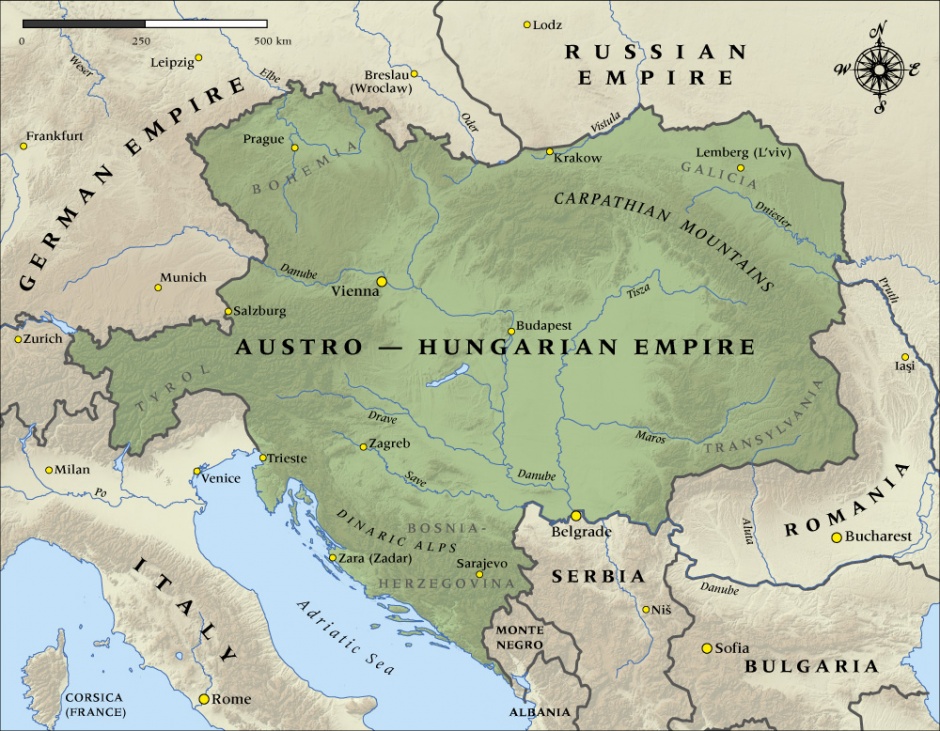
On September 10, 1919, the Treaty of St. -Germain recognized Hungary's independence from Austria. The Treaty of Trianon, signed on June 4, 1920, defined Hungary's postwar boundaries. It lost three-quarters of its prewar territory and two-thirds of its prewar population to neighboring states.In 8 AD, the western part of the territory (the so-called Transdanubia) of modern Hungary formed part of Pannonia, a province of the Roman Empire.Negotiations between the emperor and the Hungarian leaders were intensified and finally resulted in the Compromise of 1867, which created the Dual Monarchy of Austria-Hungary, also known as the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
What was the former Kingdom of Hungary : The Kingdom of Hungary was a multiethnic state from its inception until the Treaty of Trianon and it covered what is today Hungary, Slovakia, Transylvania and other parts of Romania, Carpathian Ruthenia (now part of Ukraine), Vojvodina (now part of Serbia), the territory of Burgenland (now part of Austria), Međimurje ( …
Is Hungary Slavic or Balkan
They consider themselves neither Slavic or Germanic like many nations in Europe. Western and Central Europe are usually dominated by nations speaking Germanic or the Romance (Latin) languages while the Balkans are dominated by Slavic, Balkan Romance, Albanian and Modern Greek linked linguistics.
What was Hungary called in WWII : The Kingdom of Hungary was an Axis Power during World War II, intent on regaining Hungarian-majority territory that had been lost in the Treaty of Trianon, which it mostly did in early 1941 after the First and Second Vienna Awards and after joining the German invasion of Yugoslavia.
Definition of 'Magyar'
1. a member of the people constituting the main ethnic group in Hungary. 2. the Ugric language of this people; Hungarian. adjective.
After six centuries of independent statehood (896–1526) Hungary became part of two other political entities: the Habsburg and Ottoman empires. In the 19th century it became a partner in Austria-Hungary (1867–1918).
Why did Austria split with Hungary
The more immediate reasons for the collapse of the state were World War I, the 1918 crop failure, general starvation and the economic crisis. The Austro-Hungarian Empire had additionally been weakened over time by a widening gap between Hungarian and Austrian interests.After six centuries of independent statehood (896–1526) Hungary became part of two other political entities: the Habsburg and Ottoman empires. In the 19th century it became a partner in Austria-Hungary (1867–1918).Not a Turkic language
Hungary and the Ottoman Empire shared a border for centuries and the Hungarian language picked up some Turkic loan words, but Hungarian is in the Uralic language family and is closer to Finnish and Estonian than any Turkic language. The idea that Huns were Turkic is disputed by most academics.
Procopius wrote that the Slavs "are all tall and especially strong, their skin is not very white, and their hair is neither blond nor black, but all have reddish hair". Jordanes wrote "…all of them are tall and very strong… their skin and hair are neither very dark nor light, but are ruddy of face".
Was Budapest destroyed in WWII : Budapest lay in ruins, with more than 80 percent of its buildings destroyed or damaged, with historical buildings like the Hungarian Parliament Building and the Castle among them. All seven bridges spanning the Danube were destroyed.
Do Magyars still exist : Hungarians, also known as Magyars (/ˈmæɡjɑːrz/ MAG-yarz; Hungarian: magyarok [ˈmɒɟɒrok]), are a Central European nation and an ethnic group native to Hungary (Hungarian: Magyarország) and historical Hungarian lands (i.e. belonging to the former Kingdom of Hungary) who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and …
What country calls itself Magyar
The Hungarian endonym is Magyar, which is derived from Old Hungarian Mogyër.
France – 843 CE. Austria – 976 CE. Denmark – sometime in the 10th century CE. Hungary – 1001 CE.Austria struggled to compete with the economic power of the revived Prussia. Austria could barely compete with the economic benefits of the Zollverein. Many of the German states were involved and Austria was excluded. Austria's geographical position meant that it could not trade as easily as Europe's northern states.
What is Austria-Hungary called now : Answer and Explanation: Austria-Hungary does not exist today. Its lands were divided into a number of smaller independent countries. These include all or parts of the present-day countries of Austria, Hungary, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Slovenia, Croatia, Montenegro, Serbia, Romania, Ukraine, Poland, and Italy.