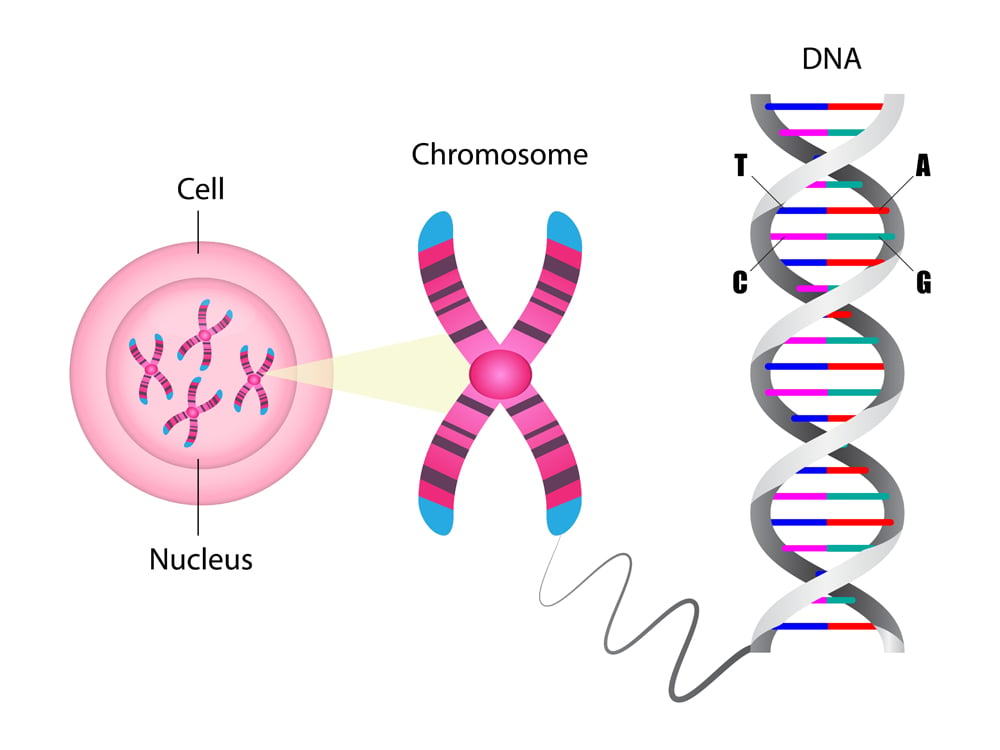
Our genetic manual holds the instructions for the proteins that make up and power our bodies. But less than 2 percent of our DNA actually codes for them. The rest — 98.5 percent of DNA sequences — is so-called “junk DNA” that scientists long thought useless.Junk DNA and non-coding DNA
According to a recent article published in American Scientist: Close to 99 percent of our genome has been historically classified as noncoding, useless "junk" DNA. Consequently, these sequences were rarely studied.In humans, only about 2% of the genome encodes proteins. Much — but not all — of the remaining 98% is evolutionary detritus. In the 1960s, researchers learned that non-coding DNA can serve vital functions, such as regulating gene action and building ribosomes.

Is 99% of our DNA the same : The completion of the Human Genome Project in 2003 confirmed humans are 99.9% identical at the DNA level and there is no genetic basis for race.
Is DNA 100% correct
They send the samples to a lab, where a specialist analyzes trace amounts of the fetus's DNA in the blood sample and compares it to the DNA in a cheek swab from the potential non-birthing parent. An NIPP is 99.9% accurate and very safe.
Why can’t DNA be 100% : You can't inherit more than half of an ancestor's DNA
You receive 50% of your genes from each of your parents, but the percentages of DNA you received from ancestors at the grandparent level and further back are not necessarily neatly divided in two with each generation.
As a result, we share roughly 90 percent of our DNA with mice, dogs, cattle, and elephants. Coming closer to home, the DNA of human beings and chimpanzees is 98 to 99 percent identical.
Junk DNA came into existence through transposition. Transposition is the movement of sections of DNA to different positions in the DNA. If this transposition activity happens in cell that makes egg or sperm, then resultant DNA is transferred into the offspring also.
What is greater than 98% of human DNA
Greater than 98% of human DNA has unknown functions. Only about 2% of the human genome contains protein-coding sequences (known as exons) and about 98% of the human genome contains non-coding sequences (known as introns).chimpanzee
The euchromatic regions of chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) genome share approximately 98% sequence similarity with the human (Homo sapiens), while the heterochromatic regions display considerable divergence.Identical twins are the only siblings who share 100 percent of their DNA. This is because identical twins are born when one zygote (formed by a sperm and egg cell) splits into two foetuses. This is quite a rare situation that only occurs in around three or four births per thousand.
Another way of understanding the 99.999% minimum Probability of Paternity is that the chance of a wrong conclusion, i.e. the true biological father is not the tested man, is at worst 1 in 100,000 and is usually 1 in millions, if not higher.
Can a DNA test be 90 percent : Paternity can be determined by highly accurate tests conducted on tissue or blood samples of the father (or alleged father), mother, and child. These tests produce accurate results in the range of between 90 and 99 percent.
How far back is 1% Ancestry : seven generations back
The chart below shows probable (but not necessarily actual) percentages of genes you may have inherited from ancestors going back four generations. At seven generations back, less than 1% of your DNA is likely to have come from any given ancestor.
Which animals DNA is 98% similar to human beings
Humans and chimps share a surprising 98.8 percent of their DNA. How can we be so similar–and yet so different
We could compare all the DNA in humans to all the DNA in chimpanzees. The easiest difference to look at is changes in individual letters of our DNA sequence. These are called single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). When you do this comparison, the two species are about 99% identical.Studies have shown that DNA evidence is 99% accurate, making it one of the most foolproof pieces of evidence you can possibly use in court. Like fingerprints, no two people have the same DNA. If a mistake occurs, it's typically because of human error.
Is 97 of DNA junk : In 2000, when scientists of the Human Genome Project presented the first rough draft of the sequence of bases, or code letters, in human DNA, the initial results appeared to confirm that the vast majority of the sequence—perhaps 97 percent of its 3.2 billion bases—had no apparent function.