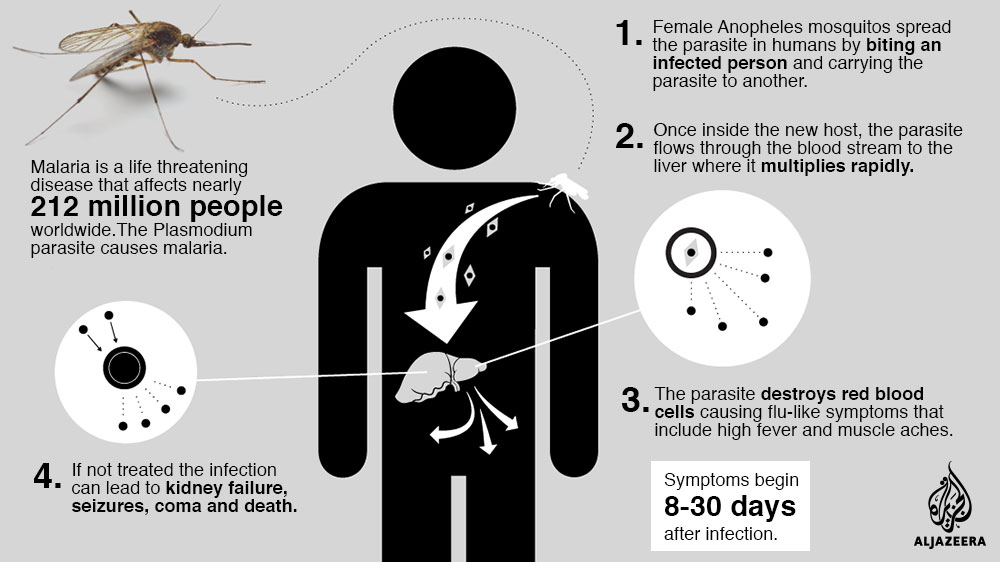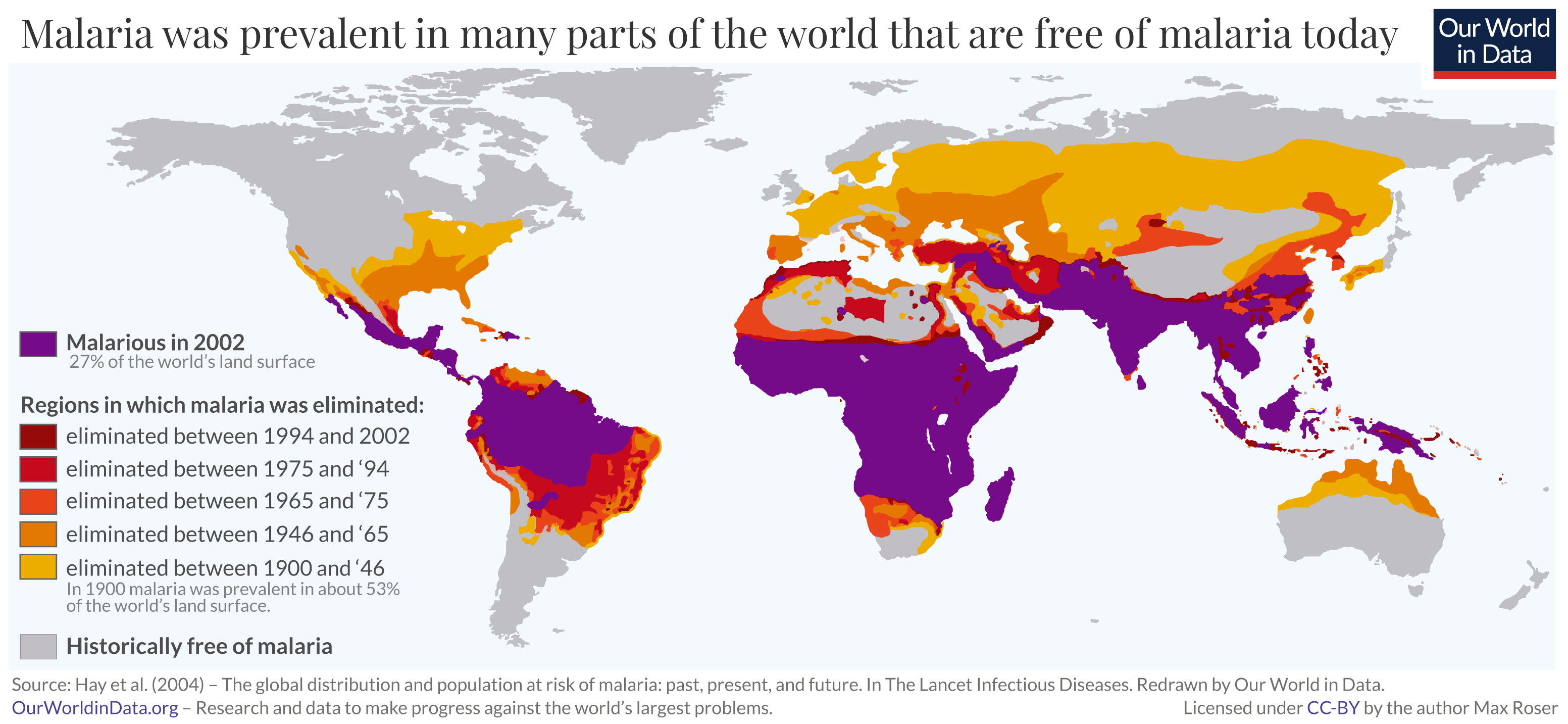
One estimate, which has been published in a 2002 Nature article, claims that malaria may have killed 50-60 billion people throughout history, or about half of all humans that have ever lived.Infection with malaria parasites may result in a wide variety of symptoms, ranging from absent or very mild symptoms to severe disease and even death. Malaria disease can be categorized as uncomplicated or severe (complicated). In general, malaria is a curable disease if diagnosed and treated promptly and correctly.Malaria can be cured in 2 weeks if diagnosed early and treated properly, but without proper treatment, those infected with malaria may recur periodically with symptoms of fever, chills.

Can malaria go away on its own : With some types of Plasmodium, malaria can disappear but return months or years later. This occurs because the parasites have dormant stages, during which there is no disease activity. However, symptoms can occur if they reactivate.
What killed the most humans in history
Table ranking "History's Most Deadly Events": Influenza pandemic (1918-19) 20-40 million deaths; black death/plague (1348-50), 20-25 million deaths, AIDS pandemic (through 2000) 21.8 million deaths, World War II (1937-45), 15.9 million deaths, and World War I (1914-18) 9.2 million deaths.
Has anyone survived malaria : Stuart Ver Wys survived severe malaria after he contracted malaria during a mission trip to Haiti. He had not taken any drugs to prevent malaria… Mariama Jones was 19 weeks pregnant when a family crisis required that she travel to her native Sierra Leone.
Probably the worst headache, body aches, and chills you could possibly imagine. It felt like I was being stung repeatedly by an electric shock gun and could barely control my movements.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes life-threatening disease. It spreads through bites from infected mosquitos. Malaria is not common in the U.S. But you can get it when you travel to other parts of the world.
What is the survival rate of malaria
Although untreated severe malaria is nearly always fatal, with timely and effective treatment, the death rate due to malaria in the US is less than 2%. Patients diagnosed with severe malaria should be treated with intravenous antimalaria medications and be closely monitored in an intensive care unit.Malaria may recur
Some varieties of the malaria parasite, which typically cause milder forms of the disease, can persist for years and cause relapses.Here are the top four infectious disease by number of deaths:
- COVID-19: 1.24 million.
- Tuberculosis: 1.13 million.
- HIV/AIDS: 630,000.
- Malaria: 620,000.
23 January 1556
While it's hard to say with certainty, by many accounts the deadliest day in human history was actually the result of a natural disaster. On the morning of 23 January 1556, a massive earthquake rocked China's Shaanxi province, at the time considered the 'cradle of Chinese civilization'.
What are the odds of surviving malaria : Malaria is a potentially fatal disease, but it is preventable and treatable. Mortality amongst travellers who catch malaria varies between 2-3%.
Has malaria killed the most people ever : The often-repeated claim that malaria killed half of all humans who ever lived is very likely an overstatement, but it is certainly the case that the mosquito-borne fever was one of the most common causes of death in human history.
How long can you survive malaria
Left untreated, P. falciparum malaria can progress to severe illness and death within 24 hours.
About 2,000 cases of malaria are diagnosed in the United States annually, mostly in returned travelers. Travelers to sub-Saharan Africa have the greatest risk of both getting malaria and dying from their infection. However, all travelers to countries where malaria is present may be at risk for infection.Malaria can be fatal, particularly when caused by the plasmodium species common in Africa.
Which country has the most malaria deaths : That's more than 1,000 children dying of malaria every day, mostly in Africa. 94% of cases and 95% of deaths were in the WHO African Region. Four countries – Nigeria (27%), the Democratic Republic of the Congo (12%), Uganda (5%) and Mozambique (4%) – accounted for almost half of all cases globally.