Few among the millions of fungal species fulfill four basic conditions necessary to infect humans: high temperature tolerance, ability to invade the human host, lysis and absorption of human tissue, and resistance to the human immune system.They are the interface between death and life — without them, the world would be buried under fallen trees, the remains of animals and infertile soil. Various fungi form intimate and intelligent partnerships with all forms of life, supporting the health of most — if not all — organisms.Fungi were some of the first complex life forms on land, mining rocks for mineral nourishment, slowly turning them into what would become soil. In the Late Ordovician era, they formed a symbiotic relationship with liverworts, the earliest plants.
Are fungi closer to plants or animals : Answer and Explanation: Fungi are more closely related to animals than plants because they are heterotrophic, like animals. Heterotrophs are organisms that are unable to make their own food through photosynthesis.
Are we closer to fungi
Genetic comparisons place fungi closer to man than to plants. The revelation is just one of many emerging new ideas about family ties in the upper reaches of the earth's 3.5-billion-year-old tree of life, in particular ties among plants and between them and other higher forms of existence.
Could cordyceps infect humans : In “The Last of Us,” a mutated Cordyceps variant begins infecting humans. But this jump from insects to people is highly implausible, says Roberts. “There are millions of different fungal and mold species out in nature that don't cause any sort of infection in humans, and this is one of them,” he explains.
Like all forms of fungus, mold is a living organism that can grow and reproduce. A look at the mold life cycle will help you understand how it can quickly spread through your home before you even realize it's there. The initial stage begins with a cell called a hypha.
Currently, only a small number of antifungal drug types exist, so resistance can severely limit treatment options. Some types of fungi, like Candida auris, can become resistant to all the antifungal drugs normally used to treat these infections.
Did humans come from fungi
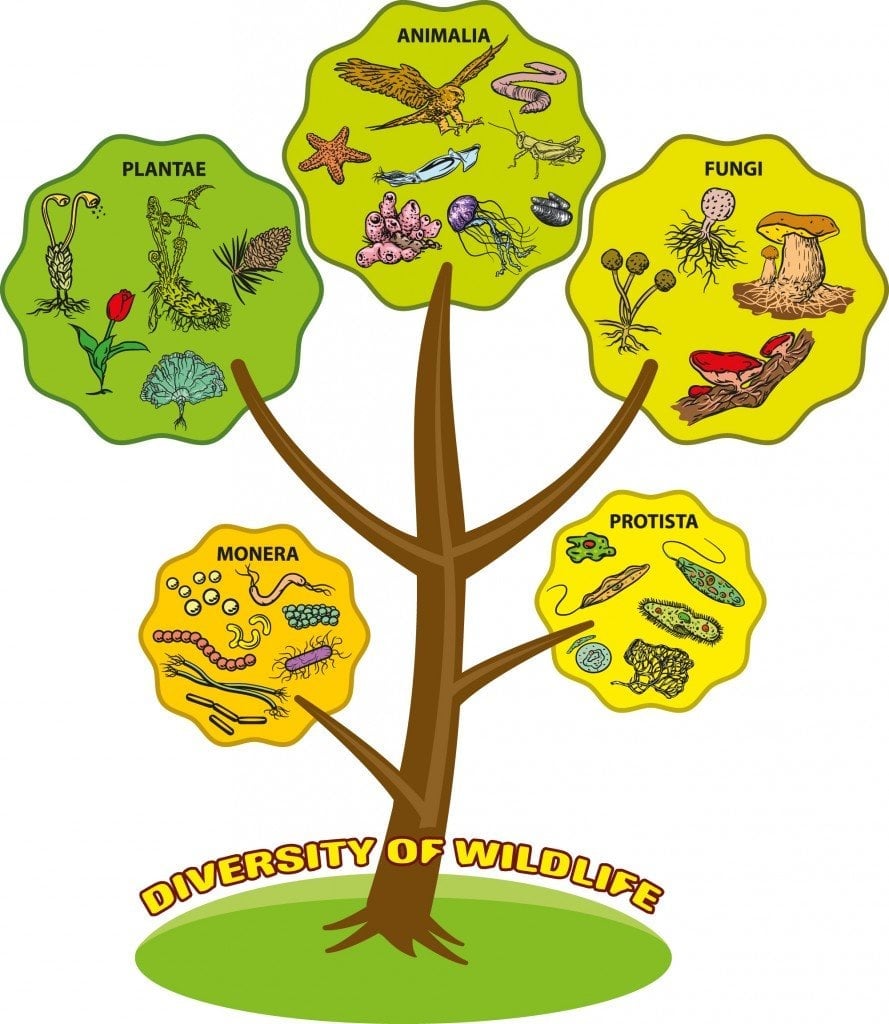
Fungi are fairly closely related to animals, but we split from fungi before we even became animals, before we even became multi-cellular organisms. Fungi and humans are both Opisthokonts, meaning that our spores/sperms have a single posterior flagellum that pushes it forward.There is one fungal species capable of infecting people that scientists think may have resulted from warming temperatures, called Candida auris. It wasn't even known to science until 2007, but in 2011 and 2012, it was suddenly found on three different continents.Computational phylogenetics comparing eukaryotes revealed that fungi are more closely related to us than to plants. Fungi and animals form a clade called opisthokonta, which is named after a single, posterior flagellum present in their last common ancestor.
Genetic comparisons place fungi closer to man than to plants. The revelation is just one of many emerging new ideas about family ties in the upper reaches of the earth's 3.5-billion-year-old tree of life, in particular ties among plants and between them and other higher forms of existence.
Are fungi like humans : As lower eukaryotes, fungi are more closely related to humans than are other microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses. With what little fungal sequence is available, homologues for 30 percent of human proteins can be found, almost twice what is known from S. cerevisiae alone.
Do fungi have DNA : Fungi are eukaryotes and have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus where the DNA is wrapped around histone proteins. A few types of fungi have structures comparable to bacterial plasmids (loops of DNA).
Is The Last of Us a possibility
Although “The Last of Us” may be more fiction than fact, Roberts says there's a sentiment of gratitude among infectious disease specialists for the rise in awareness of fungal infections. “The show might not be realistic, but pathogens like Candida auris are likely going to get more press now,” he says.
“There are no treatments for this,” he says. “No preventatives, no cures.”As you can see, mold does not die when it dries out. Instead, it enters a dormant state and can reactivate once moisture is reintroduced. Therefore, simply drying out mold-infested areas is not enough to eliminate the problem. Mold spores can still pose risks even when they appear inactive.
Are mold harmless : Exposure to damp and moldy environments may cause a variety of health effects, or none at all. Some people are sensitive to molds. For these people, exposure to molds can lead to symptoms such as stuffy nose, wheezing, and red or itchy eyes, or skin.