:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stock-market-crash-sell-off---trading-screen-in-red-104271845-565bca2f055c47558a2d17ec3563a4dd.jpg)
When a stock's price falls to zero, a shareholder's holdings in this stock become worthless. Major stock exchanges actually delist shares once they fall below specific price values. The New York Stock exchange (NYSE), for instance, will remove stocks if the share price remains below one dollar for 30 consecutive days.A drop in price to zero means the investor loses his or her entire investment: a return of -100%. To summarize, yes, a stock can lose its entire value. However, depending on the investor's position, the drop to worthlessness can be either good (short positions) or bad (long positions).For a put option buyer, the maximum loss on the option position is limited to the premium paid for the put. The maximum gain on the option position would occur if the underlying stock price fell to zero.
Can a stock be valued at zero : Certainly! Imagine you bought a company's stock for $100, hoping its value would go up. However, if the company faces serious financial problems and its stock price falls to $0, it means the company is essentially bankrupt. In this situation, you can't make money from that stock because it's worth nothing.
Can the S&P 500 go to 0
And while theoretically possible, the entire US stock market going to zero would be incredibly unlikely. It would, in fact, take a catastrophic event involving the total dissolution of the US government and economic system for this to occur.
Do I lose my money if a stock is delisted : Though delisting does not affect your ownership, shares may not hold any value post-delisting. Thus, if any of the stocks that you own get delisted, it is better to sell your shares. You can either exit the market or sell it to the company when it announces buyback.
Can a stock ever rebound after it has gone to zero Yes, but unlikely. A more typical example is the corporate shell gets zeroed and a new company is vended [sold] into the shell (the legal entity that remains after the bankruptcy) and the company begins trading again.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_INV_final-Accumulation_Feb_2021-01-fba8356738864f07b0018b19569b15b7.jpg)
A stock price of zero, however, means that the expectation of future earnings is irrevocably lost, as would be the case for a company that dissolves and ceases to do business. In order for an entire stock market to go to zero, the same would need to be true for all companies in the stock market.
Can S&P 500 go negative
The S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average both turned negative in afternoon trade ahead of a jobs report for March that could help inform the Federal Reserve's path to lower interest rates.Over the past 94 years, the S&P 500 has gone up and down each year. In fact 27% of those years had negative results.For example, on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), if a security's price closed below $1.00 for 30 consecutive trading days, that exchange would initiate the delisting process. Furthermore, the major exchanges also impose requirements related to market capitalization, minimum shareholders' equity, and revenue outputs.
If a company is delisted, you are still a shareholder, to the extent of a number of shares held. And yet, you cannot sell those shares on any exchange. However, you can sell it on the over-the-counter market. This means you can look for a buyer outside the stock exchange.
Can a stock return from zero : Sometimes when a stock goes down in value it can present an investment opportunity, but in other cases the stock could fall to zero and never recover. In the latter case, it may benefit investors to sell before the stock price falls all the way down to zero.
What happens if the S&P 500 goes to zero : A stock price of zero, however, means that the expectation of future earnings is irrevocably lost, as would be the case for a company that dissolves and ceases to do business. In order for an entire stock market to go to zero, the same would need to be true for all companies in the stock market.
Can the S&P 500 collapse
But how far could the pullback go Paul Dietrich, the chief investment strategist at B Riley Wealth Management has issued a stark warning that the S&P 500 could plummet by 44% to approximately 2,800 points.
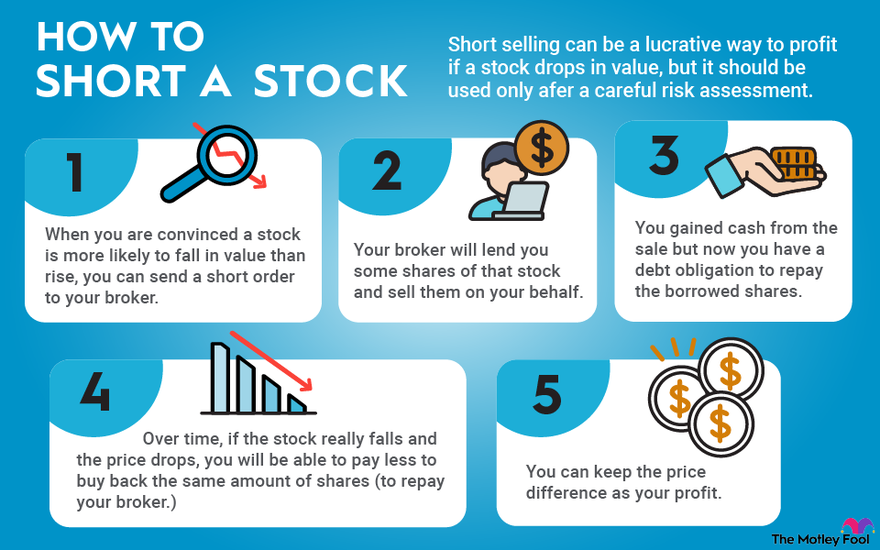
No, a stock market crash only indicates a fall in prices where a majority of investors face losses but do not completely lose all the money. The money is lost only when the positions are sold during or after the crash.For instance, say you sell 100 shares of stock short at a price of $10 per share. Your proceeds from the sale will be $1,000. If the stock goes to zero, you'll get to keep the full $1,000. However, if the stock soars to $100 per share, you'll have to spend $10,000 to buy the 100 shares back.
Is the market going to crash in 2024 : Stock market investors may be anxious, but as the old saying goes, "There's no need to panic." "While we maintain a positive view on the U.S. stock market in 2024, there are a range of risk factors that could derail the current bull market," Dilley says.





