Astronomers measure the amount of dust in the Milky Way and the dominant colors of the light we see, and they match those we find in other typical spiral galaxies. All of this adds up to give us a picture of the Milky Way, even though we can't get outside to see the whole thing.The Milky Way is visible from most dark sky locations during the year, but only on clear, moonless nights, so the viewing window is limited. As seen from the Northern Hemisphere, the Milky Way passes through eight notable constellations—Sagittarius, Scorpius, Aquila, Cygnus, Perseus, Cassiopeia, Auriga, and Gemini.Galileo Galilei
Proof of the Milky Way consisting of many stars came in 1610 when Galileo Galilei used a telescope to study the Milky Way and discovered that it is composed of a huge number of faint stars. Galileo also concluded that the appearance of the Milky Way was due to refraction of the Earth's atmosphere.
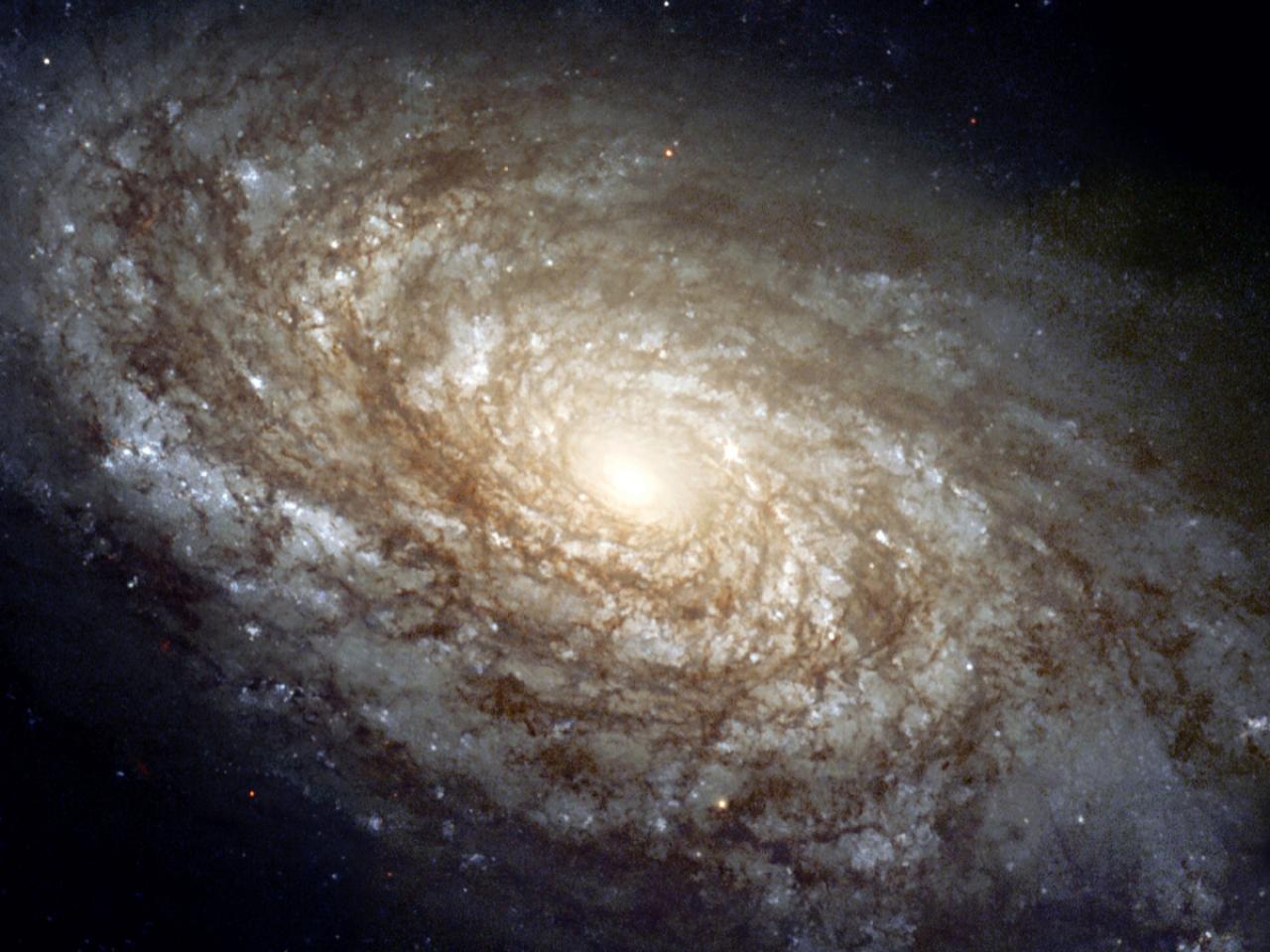
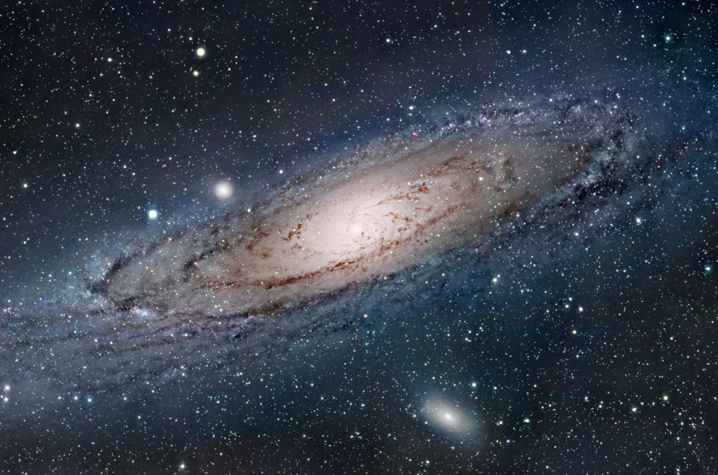
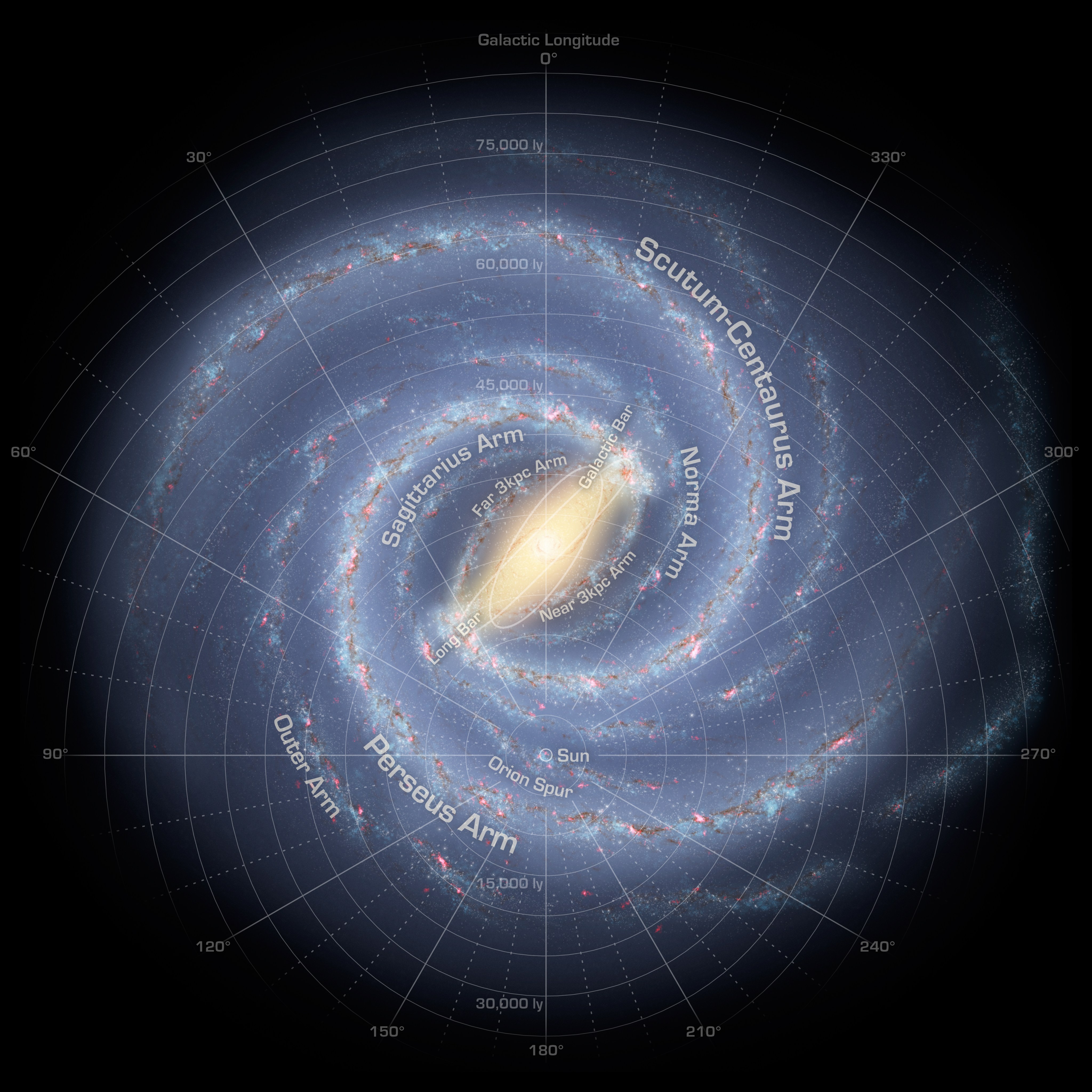
Do we really know what our galaxy looks like : Today, we know that we are looking along the plane of our spiral galaxy, consisting of at least 100 billion stars. But understanding the shape of the Milky Way proved elusive up until the 20th century. The problem is we can't get a bird's eye view of our galaxy because our solar system is buried within the galaxy.
How did we get a picture of Milky Way
The answer, of course, is we don't have any such images, at least not photographic images. All pictures you see of the Milky Way in its entirety are artistic impressions or computer renderings, like this one from NASA. But this just leads to another question: How do we know what our galaxy looks like from the outside
Have humans seen the Milky Way : Most scientists speculate the Milky Way is a barred galaxy, but we can't confirm this. That being said, even today less than 50% of the world lives in cities, so most people probably have seen a part of the Milky Way.
So, to sum up, looking inwards into the Milky Way, our visibility is very restricted to the nearest 1,000–2,000 ly (while the MW disk's radius is 50,000 to 90,000 ly and we're about 27,000 ly on this side of center, but only the brightest stars are visible from more than about 400 ly away.
No human-made objects have left the Milky Way galaxy. However, the Voyager 1 spacecraft, launched in 1977, is currently the farthest human-made object and has entered interstellar space after passing through the heliopause, the boundary of the Sun's influence.
How old is the oldest Milky Way
The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy around 13.6 billion years old with large pivoting arms stretching out across the cosmos. Our home galaxy's disk is about 100,000 light-years in diameter and just 1000 light-years thick, according to Las Cumbres Observatory.You may think that you need a telescope to be a stargazer, but that's not true. There are lots of amazing things you can see with nothing but your eyes, such as constellations, planets, the Milky Way, meteor showers, zodiacal light or even the aurora borealis (northern lights).Finnish astrophotographer J-P Metsavainio spent 1,250 hours over the course of about 12 years creating a single image that reveals the magnificent beauty of the entire Milky Way galaxy.
The reason that the stars do not show up on the film is that the stars are so dim that the camera cannot gather enough of their light in a short exposure. Our eyes are a lot more sensitive to light than photographic film. A good example of this is when we take a picture with a camera that is back lighted.
How rare is it to see the Milky Way : The Milky Way, the brilliant river of stars that has dominated the night sky and human imaginations since time immemorial, is but a faded memory to one-third of humanity and 80 percent of Americans, according to a new global atlas of light pollution produced by Italian and American scientists.
Why can’t we see the Milky Way anymore : Artificial light pollutes the night sky for more than 80% of the world's population, and one third of humanity cannot see the Milky Way at night due to the luminescent glow of artificial light, according to a new world atlas that attempts to quantify the global impact of light pollution.
Why can’t we take pictures of the Milky Way
We can't take a picture of the Milky Way from the outside, only edge on, because we are inside the Milky Way and we can't go above or below it to take a picture.
The Milky Way still has star formation regions, most famously the relatively nearby Orion Nebula. Nevertheless, astronomers have long concluded it is far past its best years, with a rate of star formation that might be classed as “mostly dead” – just one to two stars a year by some estimates, two to five in others.For the moment, sending humans to the edge of interstellar space, let alone across the cosmic void to other stars, remains firmly in the realm of science fiction. But scientists and engineers are developing skills and technologies that might help us get there one day.
How long do galaxies live : Four billion years from now, our galaxy, the Milky Way, will collide with our large spiraled neighbor, Andromeda. The galaxies as we know them will not survive. In fact, our solar system is going to outlive our galaxy.